Number Systems
Introduction to Number Systems
A number system defines a set of values used to represent quantities. In digital electronics, number systems are essential for designing and analyzing circuits.
Types of Number Systems
– Decimal System (Base-10):
– Uses digits: 0, 1, 2, 3, …, 9.
– Base = 10.
– Each digit has a place value: 10^n .
– Binary System (Base-2):
– Uses digits: 0, 1.
– Base = 2.
– Each digit has a place value: 2^n .
– Commonly used in digital electronics.
– Octal System (Base-8):
– Uses digits: 0, 1, 2, …, 7.
– Base = 8.
– Each digit has a place value: 8^n .
– Hexadecimal System (Base-16):
– Uses digits: 0–9 and letters: A, B, C, D, E, F (representing 10–15).
– Base = 16.
– Each digit has a place value: 16^n .
Conversions Between Number Systems
Decimal to Binary:
– Divide the number by 2.
– Write the remainder.
– Continue until the quotient is 0.
– Reverse the remainders.
Example:

Binary to Decimal:
– Multiply each bit by 2^n , where n is the bit’s position from the right (starting at 0).
– Add the results.
Example :
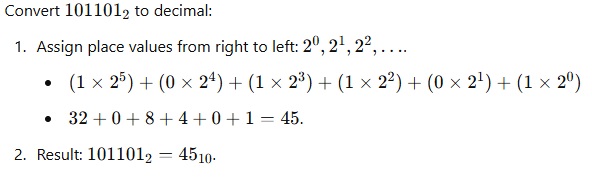
Decimal to Octal:
– Divide the number by 8 and note the remainders.
– Reverse the remainders.
Example :

Octal to Decimal:
– Multiply each bit by 8^n , where n is the bit’s position from the right (starting at 0).
– Add the results.
Example :
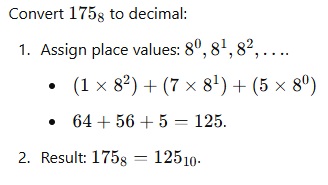
Decimal to Hexadecimal:
– Divide the number by 16 and note the remainders.
– Convert remainders above 9 to their hexadecimal equivalent.
– Reverse the remainders.
Example :

Hexadecimal to Decimal:
– Multiply each bit by 16^n , where n is the bit’s position from the right (starting at 0).
– Add the results.
Example :
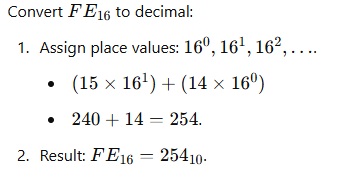
Binary to Octal:
– Group binary digits into sets of 3 (starting from the right).
– Convert each group to its octal equivalent.
Example :
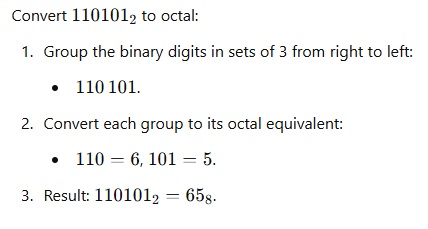
Binary to Hexadecimal:
– Group binary digits into sets of 4 (starting from the right).
– Convert each group to its hexadecimal equivalent.
Example :

Arithmetic Operations in Number Systems
Binary Addition:
– Follows these rules:
– 0 + 0 = 0
– 0 + 1 = 1
– 1 + 1 = 10 (carry 1)
– 1 + 1 + 1 = 11 (carry 1)
– Example: 1011 + 1101 = 11000 .
Binary Subtraction:
– Use the borrow method.
– Rules:
– 0 – 0 = 0
– 1 – 0 = 1
– 1 – 1 = 0
– 0 – 1 = 1 (borrow 1 from the next higher bit).
Binary Multiplication:
– Follows these rules:
– 0 * 0 = 0
– 0 * 1 = 0
– 1 * 1 = 1
– Example: 101 * 11 = 1111 .
Binary Division:
– Similar to decimal long division but using binary numbers.
Applications of Number Systems
Binary systems are used in:
– Digital circuits and systems.
– Microprocessors and microcontrollers.
– Data encoding and storage.
– Network communication protocols.

